Strategic Implementation
Alignment
Abstract
This article
focuses on strategic implementation and how action plans is done to create
consistency checks and face potential resistance.
Overview
Strategic
implementation is not an easy task and due to poor time and efforts are devoted
to it ,poor implementation leads to failure in execution phase. Since
implementations is an evolutionary process and takes is time consuming a
successful actions plans should be adopted to allow flexibility , risks and
contingency plans. It is often helpful to break out
actions into long term and short term plans. In order to allocate the firm’s
resources in an optimal manner 7-S model will be used to build blueprint of an
aligned organization, the result will highlight areas need to be changed. In general most
people in an organization will wary of change, through this article we will
move on approaches and tactics leaders will follow to overcome the resistance
In early 80’s group of
consultants and professors created a model named 7-S for effectively organizing
a company. The 7 S’s refer to Strategy, Structure, Systems, Staffing, Skills,
Style and Shared Values.
To be successful high degree of
fit between variable must occur, any variable will change others will change
also.
Strategy - firm’s strategy
should take into account resources, competitors, customers and supplier in
order to create Competitive advantage.
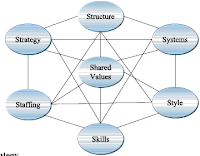 Structure - Structure is
the way in which different units of the company are divided and how authority
is organized. Optimal structure will depend on many factors. Four common
structures include functional, divisional, matrix and network.
Structure - Structure is
the way in which different units of the company are divided and how authority
is organized. Optimal structure will depend on many factors. Four common
structures include functional, divisional, matrix and network.
1-
Functional - the firm is broken
out into major functions like manufacturing, R&D, and HR,etc. each of these functional areas maybe have a
manager. This works best for firms that are small and in stable environment.
2-
Divisional - This organizational
structure breaks the firms up into specialized divisions based on
characteristics such as product lines, geography or market segment. This model
is best suited for large firms, the weaknesses of this model is integration
between divisions is minimal.
Systems - The way a
firm’s procedures and processes are organized can help support the strategy.
These activities can be both formal and informal.
The
way the systems in an organization are aligned governs almost every activity an
employee is involved with.
Staffing - the approach
the company take through HR activities is vital to the success of the company.
Personnel should be developed and monitored in order to assure they are aligned
with the company’s vision.
Skills - The skills of a
company are usually identified as what the firm does best. This skills can be
technology, systems, management processes, innovation or even customer service
procedures.
Style - style is norms
employees follow and how they work and interact with each other. What manager
say is important as procedures. The style of a firm depends on many factors and
can change over time. The style of an organization can also impact how well
change is received.
Shared values: values is an unwritten set of ideas that guides the firm.
These values are rooted in the mission of the company and influence managers
and employees in everyday activities.
Applications
Senior managers should take time
to study the current state of each of the elements and then consider the ideal
picture of what each element should look like. Based on this analysis, action
plans can be developed to get the elements where they need to be. We will next
turn on tips when dealing with change results from strategy implementing.
Managing change
Strategic implementations are
always accompanied by significant changes these changes are often faced with
resistance. The next section we will talk about tactics and strategies to
overcome resistance.
Strategies for
implementing change
There are two extremes in
implementation strategy. At one end of the spectrum is a directive approach.
This strategy is commonly referred to as Bold Strokes. On the other end
is a participative approach referred to as the Long March.
Bold stroke - When the firm
is in crisis, this is the optimal model. The Bold Strokes model attempts to
quickly overcome resistance with little involvement from the others. This model
is best suited for leaders who have clear plan, trusted and have a good support
form shareholders. The benefits of this model include quick results with less
time for opposition to build.
Long March - Participation
is the hallmark of this model. The goal is to minimize resistance. This
framework is best suited for leaders that lack credibility, power or trust. It
can also provide a leader time to gather knowledge if unfamiliar with
organization, products or customers.
Resistance
Opposition can come in many
forms. Diagnosing resistance is vital to overcoming it. In order to prepare for
this potential conflict, managers should be aware of the reasons for resisting
change. We will talk next about reasons for resistance and later on about tactics to overcome it.
1-
Self interest -the person feels
they lose something of value if change is implemented
2-
Misunderstanding or lack of
trust -the may resist because they don’t understand it or not totally told
about the implications of change.
3-
Different assessments of
problems – employee may assess the situation differently form the leader and
feel its not best interest for the company
4-
Low tolerance of change –part of
human nature is to fear change.
Now we will turn our attention
to the six tactics to attack resistance.
1-
Mandate -When speed is essential
and the leader possesses considerable power.it is risky if it leaves
dissatisfaction with leader.
2-
Include Resistors in
Designing/Implementing Change – When other tactics do not work or are too
expensive, consider inviting resistors to help with the planning. This can be a
relatively quick and inexpensive solution to resistance problems.
3-
Negotiation and Agreement – When
some group will clearly lose out in a change and when that group has
considerable power.
4-
Facilitation and Support – When
resistance stems from adjustment problems and fear of change, it is best to
take a supportive stance. This could include training, listening or giving time
off. However it can be expensive and time consuming and may fail.
5-
Participation and Involvement –
When leaders do not have all the information they need to design the change and
when others have considerable power to resist, participatory tactics are
necessary. This biggest downside to this
strategy is that it is very time consuming if participators design an
inappropriate change.
6-
Education and Communication –
When there is a lack of information or information/analysis is misunderstood,
the organization should focus on communication. However, educating and
communicating require significant time and effort.
Change
implementation
We will talk now about 8-step
program for successfully implementing change. This program takes into account
alignment and resistance issues.
1-
Establish sense of urgency
–communicate the importance of change.
2-
Form Powerful Guiding Coalitions
– Major change requires support from the key senior managers in order to
mitigate opposition and resistance.
3-
Create a Vision – Create a
picture of the future that is easily communicated to constituents both inside
the firm (employees) and outside (customers, stockholders).
4-
Communicate Vision – Without
credible communication, and a lot of it, the hearts and minds of the troops
will never be captured.
5-
Remove Obstacles – Align
structure, reporting lines and systems with the new vision. In some cases, the
obstacle might be a person or group of people.
6-
Plan for and Create Short-Term
Wins – If there is not immediate action, then there is the risk that you will
lose momentum. Without short-term gains, too many people may give up.
7-
Consolidate Improvements and
Produce More Change – Do not declare victory too soon, instead use successful
short term wins to build credibility and ensure that changes are lasting.
8-
Institutionalize Changes into
Organizational Structure – Deliberately show people how the changes have helped
improve performance. Ensure the next generation of mangers embodies the new
approach.
Conclusion
Strategic implementation is a very complex process. It needs
to be driven hierarchal staring from the top management level to the operation
level, the strategic implementation should follow a scientific process at all
its phases. This implementations should have a defined goals and objectives.
rules and policies should be
set to achieve these goals. in order to overcome obstacles that will
face the management they have to work on a systematic procedures dealing with
this kind of changes these obstacles are
mainly implied by the resistances to change. That’s why managers should always
look every day for new approaches in dealing with cultural changes.

Comments
Post a Comment